Ransomware is a type of malware designed to encrypt users’ files or lock their operating systems so attackers can demand a ransom payment. According to a 2016 Symantec report, the average ransom demand is almost $700 and “consumers are the most likely victims of ransomware, accounting for 57 percent of all infections between January 2015 and April 2016.”
Similar to a phishing attack, ransomware executes when a user is lured to click on an infected link or e-mail attachment or to download a file or software drive while visiting a rogue website. Sophisticated social engineering techniques are used to entice users to take the desired action; examples include
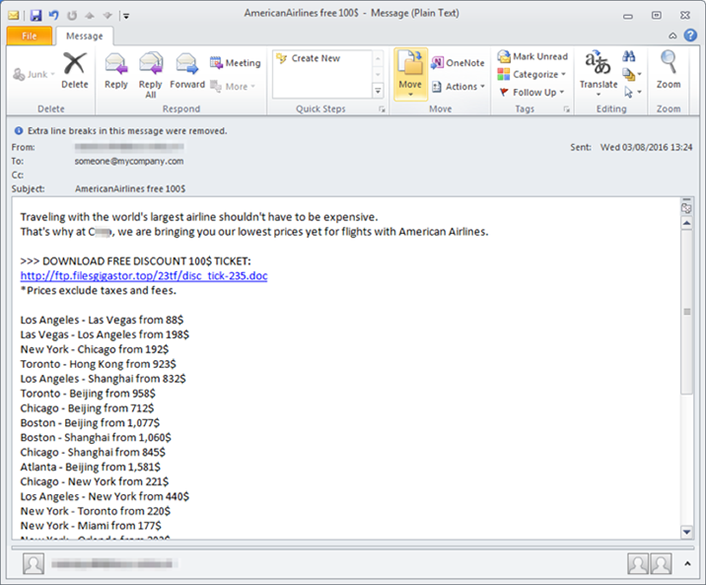
- an embedded malicious link in an e-mail offers a cheap airfare ticket (see figure 1);
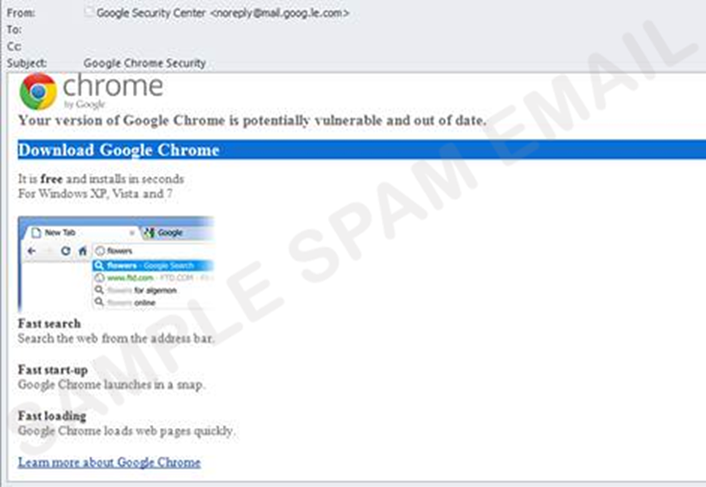
- an e-mail that appears to be from Google Chrome or Facebook invites recipients to click on an image to update their web browser (see figure 2); or
- a well-crafted website mimics a legitimate website and prompts users to download a file or install an update that locks their PC or laptop.
To avoid becoming a victim of ransomware, users can follow these tips:
- Report suspicious emails. Report any suspicious emails to report-phish@osu.edu.
- Avoid clicking on unverified e-mail links or attachments. Suspicious links might carry ransomware (such as the CryptoLocker Trojan).
- Use e-mail filtering options whenever possible. E-mail or spam filtering can stop a malicious message from reaching your inbox.
- Install and maintain up-to-date antivirus software. Keeping your operating system updated with the latest virus definitions will ensure that your security software can detect the latest malware variations.
- Update all devices, software, and plug-ins on a regular basis. Check for operating system, software, and plug-in updates often — or, if possible, set up automatic updates — to minimize the likelihood of someone holding your computer or files for ransom.
- Back up your files. Back up the files on your computer, laptop, or mobile devices frequently so you don’t have to pay the ransom to access locked files.

